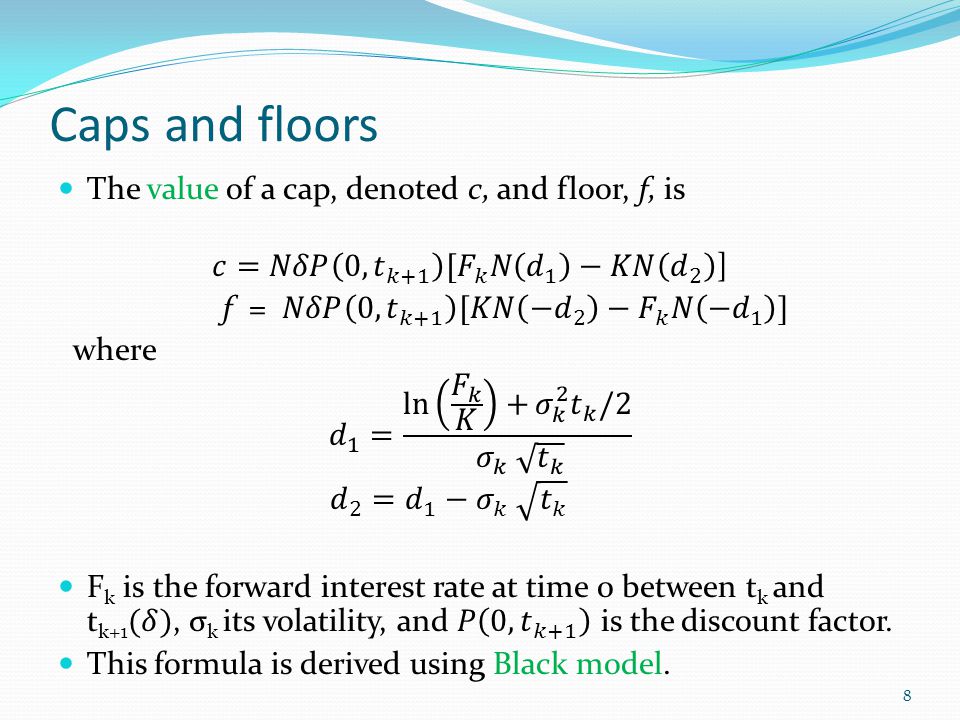
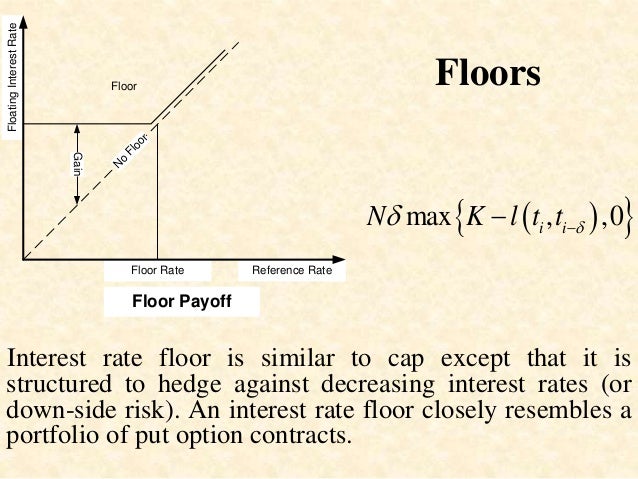
Interest rate floors and interest rate caps are levels used by varying market participants to hedge risks associated with floating rate loan products.
Interest rate caps and floors.
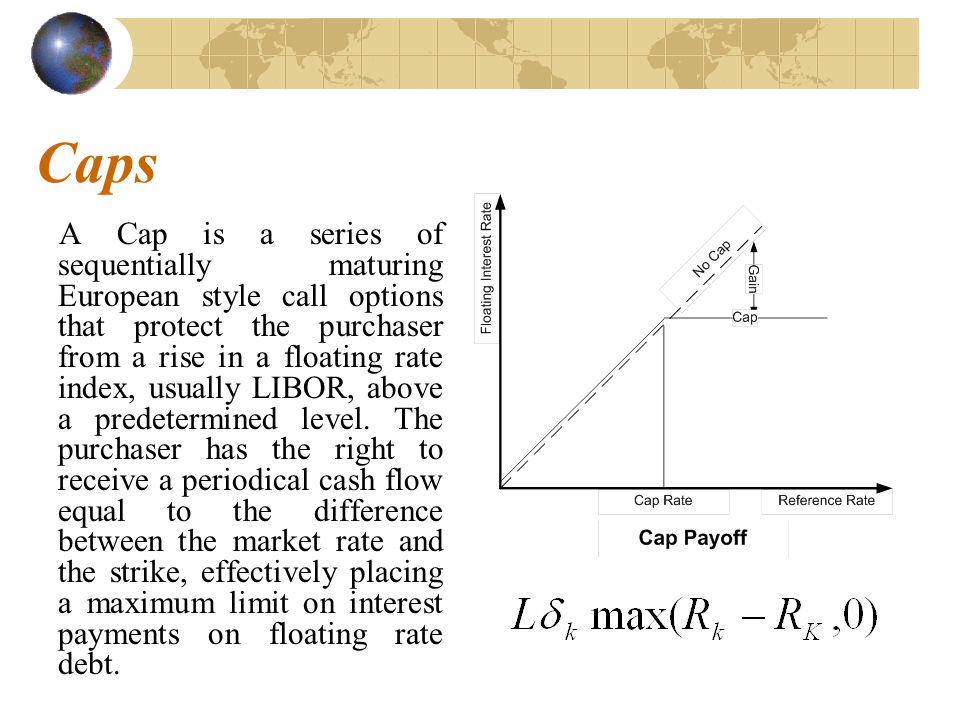
An interest rate cap is an otc derivative where the buyer receives payments at the end of each period when the interest rate exceeds the strike whereas an interest rate floor is a similar contract where the buyer receives payments at the end of each period when the interest rate is below the strike.
In other words the.
Interest rates standard options are caps and floors the cap guarantees a maximum rate to the buyer.
Interest rate caps and floors are option like contracts which are customized and negotiated by two parties.
Similarly rate floors protect the banks profit margins if rates go into the tank.
Caps and floors are based on interest rates and have multiple settlement dates a single data cap is a caplet and a single date floor is a floorlet.
In both products the buyer of the contract.
It is simply a series of call options on a floating interest rate index usually 3 or 6 month libor.
Interest rate caps and floors an interest rate cap establishes a ceiling on interest payments.
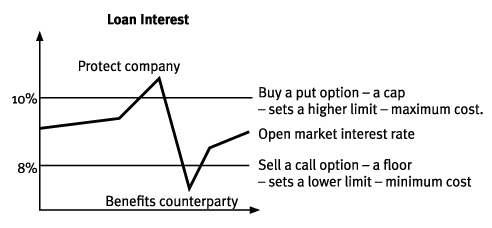
Caps floors and collars 2 interest rate caps a cap provides a guarantee to the issuer of a floating or variable rate note or adjustable rate mortgage that the coupon payment each period will be no higher than a certain amount.
A cap is an option.
Borrowers are interested by caps since they set a maximum paid interest cost.
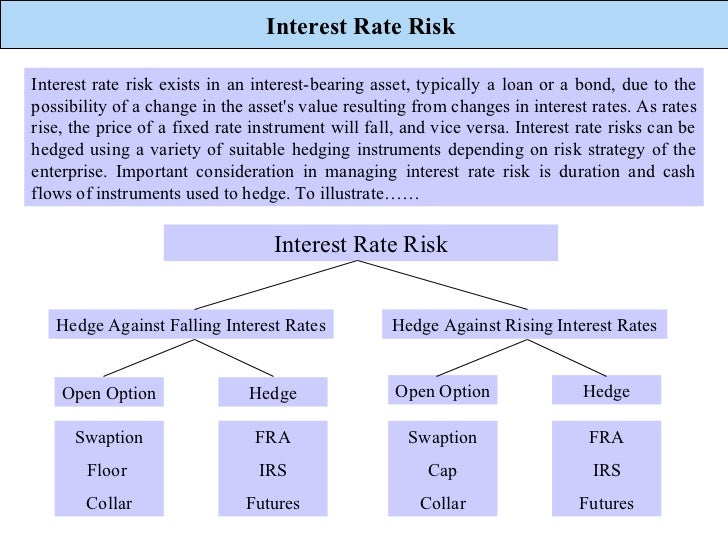
Caps and floors can be used to hedgeagainst interest rate fluctuations.
Caps and floors are like calls and puts and they are related through a parity relation which relates them to the value of a corresponding swap.
Investopedia delivers a succinct explanation.
An interest rate floor is an agreement between the seller or provider of the floor and an investor which guarantees that the investor s floating rate of return will not fall below a specified level over an agreed period of time.
An interest rate floor is an agreed upon rate in the lower range of rates associated with a floating rate loan product.
Interest rate floors are often used in the adjustable rate mortgage arm market.
For example a borrower who is paying the libor rate on a loan can protect himself against a rise in rates by buying a cap at 2 5.
On the other hand if you invested in a floating rate note and receive floating rates you ll want to protect yourself against too low rates.
It has value only when the rate is above the guaranteed rate otherwise it is worthless.










:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-180734345-ec5247651d704f57a7117eee952be492.jpg)